Code Craftsmanship
Tests
Implementing features is only one part of the development process. The other part is making sure that the features work as expected. This is where tests come in.
Tests are crucial for the development of a software project for multiple reasons:
- avoid bugs and regressions
- help to refactor the codebase
- document the codebase
Test coverage
With a good test coverage, your velocity will be higher. You will be more confident when adding more features or refactoring existing code because you will have less chance to introduce undetected bugs and regressions. You will also be able to refactor your codebase without introducing bugs.
A lot of tools exist to measure the test coverage of your codebase:
It is also important to check the different sections of the coverage reports like branch, function, line and statement coverage. A high statement coverage does not mean that the codebase is well tested. You also need to have a high branch coverage. A high branch coverage means that you have tested all the different paths of your codebase.
----------------------------|---------|----------|---------|---------|-------------------
File | % Stmts | % Branch | % Funcs | % Lines | Uncovered Line #s
----------------------------|---------|----------|---------|---------|-------------------
All files | 98.78 | 89.47 | 100 | 98.68 |
__test__ | 85.71 | 50 | 100 | 85.71 |
unlogger.js | 85.71 | 50 | 100 | 85.71 | 7
linux/scan | 100 | 83.33 | 100 | 100 |
command.js | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
parser.js | 100 | 75 | 100 | 100 | 43
macOS/connect | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
command.js | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
macOS/current-connections | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
command.js | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
parser.js | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
----------------------------|---------|----------|---------|---------|-------------------
Test automation
If the tests are run only manually by devs, there are a lot of chances that they will not be run frequently. This is why it is important to automate the tests.
Setup your CI/CD pipeline to run the tests on every commit. This will allow you to catch bugs and regressions early in the development process. It will also allow you to catch bugs and regressions introduced by other devs.
Some of them are integrated into your CI/CD pipeline and will fail the build if the test coverage is not high enough. They can fail if the global test coverage is below a threshold or if the test coverage of any new file is below a threshold. This is a good way to enforce a good test coverage.
Pyramid of tests
There are different types of tests that you can use to test your codebase. The most common types of tests are:
- unit tests
- integration tests
- end-to-end tests
In the ideal world, only end-to-end tests would be enough to test your codebase. But in the real world, it is not possible to have a good test coverage with only end-to-end tests. They are slow to run, not always stable, and hard to maintain.
The most common way to test your codebase is to use a mix of different types of tests following the strategy of the pyramid of tests.
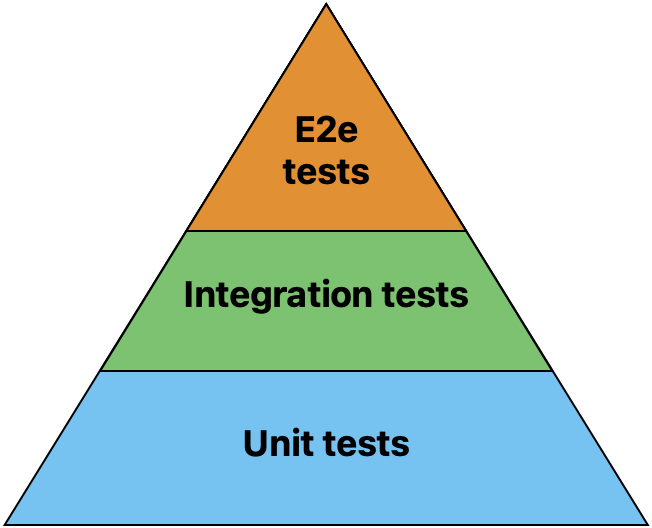
This pyramid represents the amount of tests you should add to your code: a majority of unit tests, a smaller amount of integration tests, and an even smaller amount of end-to-end tests.
Unit tests
Unit tests are tests that check the behavior of a small part of your codebase. They are the fastest to run and the cheapest to write. They are also the most stable. The challenge is to write them maintainable enough so you don't need to rewrite them every time you refactor your codebase.
Our best combo for the moment is Jest for the test runner and React Testing Library for the testing library.
End-to-end tests
End-to-end tests are tests that check the behavior of your application from the user's perspective. They are the most expensive tests to write and maintain. They are also the slowest to run. But they are very important since they are the only one to check the behavior of your application from the user's perspective.
From our experience, Playwright is the best tool to write end-to-end tests. It is very easy to use and very stable.
Accessibility tests
Nowadays, accessibility is very important. It may be useful to run some automated accessibility tests on your application. They won't cover everything but they will catch a lot of standard issues.
Playwright can be used to write accessibility tests: https://playwright.dev/docs/accessibility-testing.
For more details about accessibility, please refer to the dedicated section of this guide.
Visual tests
Visual tests are a type of test that checks the visual aspect of your application. The goal is to take a screenshot of a part of the application before the changes and after the changes. If there are differences between the two screenshots, the test will fail. They are very useful since they can cover a lot of features with a small amount of tests. However they are harder to maintain since sometimes you really want to have a visual difference between the two screenshots like when you introduce a new feature.
You can use Playwright to write visual tests: https://www.browsercat.com/post/ultimate-guide-visual-testing-playwright.
AAA pattern
When writing tests, it is important to follow the AAA pattern:
- Arrange: set up the test environment
- Act: execute the code to be tested
- Assert: check the result
This pattern will make your tests more readable and maintainable.